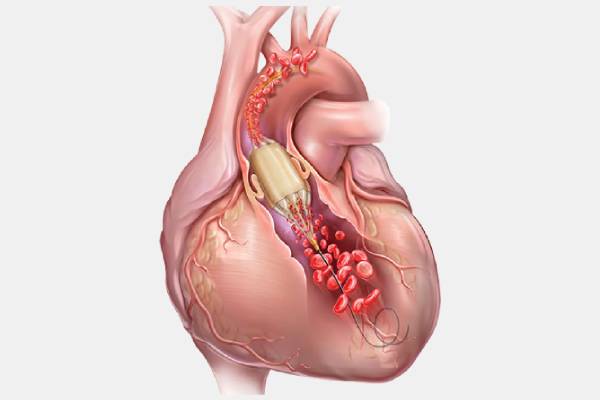
The balloon valvuloplasty is done specifically on infants who are suffering from heart disease(valvular disorders). It is done by placing a catheter through the blood vessel into the heart. The balloon is placed at the tip of the catheter. When it is blown, it forces the leaflets of the valves(cusps) to open. The balloon valvuloplasty is done in mitral, aortic, or tricuspid valves. The heart valves are responsible for sending blood to the pulmonary artery for oxygenation of the blood and transferring that oxygen-rich blood to the heart.
The Heart Valves
The heart consists of 4 valves that are responsible for the passage of blood to the heart and from the heart to other organs of the body :-
Mitral valve, also known as the bicuspid valve is one of the four valves of the heart. It is located between the upper left and lower left chambers of the heart. Also known as the bicuspid valve, the mitral valve is the only valve that has two flaps or cusps instead of three. The valve opens and closes based on the pressure differences in the upper and lower left heart chambers. The leaflet opens when there is greater pressure in the upper left chamber(left atriums) and closes when there is greater pressure on the lower left chamber (left ventricle). All of this happens within the duration of our heartbeat. The upper left chamber of the heart receives blood rich in oxygen from the pulmonary veins situated in the lungs. When the upper left heart chamber is filled with oxygen-rich blood, the mitral valve opens and blood flows to the lower left heart chamber. After transferring the blood to the lower left heart chamber, the mitral valve closes immediately to prevent regurgitation.
Also known as the right atrioventricular valve, the tricuspid valve is a boundary existing between the upper right heart chamber and the lower right heart chamber. The tricuspid valve is responsible for the transformation of deoxygenated blood into oxygen-rich blood. The blood flows from the upper right heart chamber to the lower right heart chamber and it then exits the heart through the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery then transfers blood to the lungs for its oxygenation. The tricuspid valve is named so because it has three flaps or leaflets or cusps that, after receiving blood from the upper right chamber of the heart (right atrium), closes immediately to prevent blood from flowing back to the right atrium, that is, it prevents tricuspid regurgitation. The tricuspid valve is located above the lower right heart chamber, on the right dorsal side of the heart.
Pulmonic valve, also known as the pulmonary valve is the valve that helps circulate blood in the body. The pulmonary valve is located between the lower right heart chamber and the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary valve opens when the pressure in the lower right heart chamber(right ventricle) rises above the pressure in the pulmonary artery and the valve closes on,y when the pressure in the right ventricle drops rapidly. Regurgitation cannot take place in the pulmonary valve since it is a unidirectional valve, that is, in the case of the pulmonary valve, blood cannot flow back into the heart.
The aortic valve is the last valve of the heart, located between the lower left chamber of the heart and the aorta. The aorta is the largest artery in the body. This is one of the most important structures of the circulatory system since it originates from the lower left heart chamber and extends to the abdomen where it transports oxygenated blood to all parts of the body. The aortic valve opens when pressure rises in the lower left heart chamber(left ventricle), allowing the passage of blood to exit from the heart to the aorta where it gets distributed to all the organs of the body. When the pressure in the left ventricle drops the aortic valve closes
Who Needs A Balloon Valvuloplasty
Symptoms Of Valvular Heart Disease
Types Of Balloon Valvuloplasty
What To Expect Before The Procedure
What To Expect During The Procedure
What To Expect After The Procedure
The faculty of Dr. Swapnil Mate's Cardiology clinic includes experienced cardiologists, cardiac surgeons, cardiac imaging specialists, a preventive cardiology team, experienced pediatric cardiac surgeons and assisting surgeons, physical therapists, nutritionists, geneticists, child-life specialists, a multidisciplinary interventional cardiology team, and a group of pathologists who run by tests and give the proper cause of diseases. The cardiologists and surgeons recommend the ideal surgery to the patients. They mention the advantages and risks associated with the surgeries they plan to do on them. Together, they provide services that cater to their needs. Consult Dr. Swapnil Mate for the best medical assistance.
